快速排序(Quicksort)是对冒泡排序的一种改进,又称划分交换排序(partition-exchange sort。
快速排序使用分治法(Divide and conquer)策略来把一个序列(list)分为两个子序列(sub-lists)
排序效率
在平均状况下,排序n个项目要Ο(n log n)次比较。在最坏状况下则需要Ο(n2)次比较,但这种状况并不常见。事实上,快速排序通常明显比其他Ο(n log n)算法更快,因为它的内部循环(inner loop)可以在大部分的架构上很有效率地被实现出来。
最差时间复杂度 Ο(n2)
最优时间复杂度 Ο(n log n)
平均时间复杂度Ο(n log n)
最差空间复杂度 根据实现的方式不同而不同
public static void main(String[] args) {
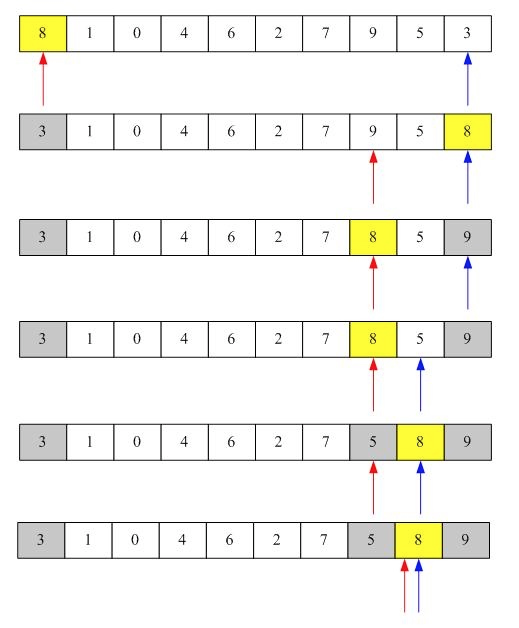
int [] arr = {8,1,0,4,6,2,7,9,5,3};
quickSort(arr,0,arr.length-1);
for(int i :arr){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static void quickSort(int[]arr,int low,int high){
if (low < high) {
int middle = getMiddle(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, middle - 1);
quickSort(arr, middle + 1, high);
}
}
public static int getMiddle(int[] list, int low, int high) {
int tmp = list[low];
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && list[high] >= tmp) {
high--;
}
list[low] = list[high];
while (low < high && list[low] <= tmp) {
low++;
}
list[high] = list[low];
}
list[low] = tmp;
return low;
}
 |
|---|
取8为中值,红色箭头表示low,绿色箭头表示high
从high开始向前扫描到第一个比8小的值与8交换。
从low向后扫描第一比8大的值与8交换。
重复①②过程只到,high=low完成一次快速排序,然后递归子序列。